For decades, traffic congestion has been the scourge of modern urban existence. It represents a colossal drain on economies, a significant source of environmental pollution, and a daily frustration for billions of commuters worldwide. The traditional solutions building more roads, implementing costly public transit projects, or encouraging carpooling have offered only marginal, often temporary relief. However, we are now standing at the precipice of a transformative era where Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not merely alleviating traffic but is fundamentally engineering its permanent elimination. This is not a futuristic fantasy; it is an operational reality taking shape in cities across the globe. AI’s integration into transportation networks is creating a paradigm shift from reactive, chaotic systems to proactive, intelligent ecosystems that optimize mobility in real-time. This comprehensive analysis delves into the multifaceted mechanisms through which AI is achieving this monumental feat, exploring the underlying technologies, current implementations, and the profound future implications for our cities and societies.
The Core Pillars: How AI Decongests Our Roadways
The eradication of traffic jams through AI is not the result of a single technology, but rather a synergistic convergence of several advanced systems working in harmony. Understanding these pillars is key to appreciating the depth of this revolution.
A. Predictive Analytics and Big Data Processing
At the heart of intelligent traffic management lies AI’s unparalleled ability to consume and interpret vast, heterogeneous datasets. Modern systems ingest real-time information from a myriad of sources:
-
GPS pings from millions of connected vehicles and smartphones.
-
Live camera feeds from intersections and major corridors.
-
Data from embedded road sensors (IoT devices).
-
Weather reports, event schedules, and social media signals.
-
Historical traffic pattern databases.
Machine Learning algorithms, particularly deep learning models, analyze this data deluge to predict traffic conditions with astonishing accuracy. They can forecast congestion 30, 60, or even 90 minutes before it forms, identifying potential trigger points like a sudden surge in vehicles heading toward a stadium or the ripple effect of a minor accident. This predictive capability shifts traffic management from a reactive discipline (“there’s a jam, let’s adjust signals”) to a proactive science (“a jam will form here in 20 minutes, let’s prevent it by pre-emptively rerouting traffic”).
B. Intelligent and Adaptive Traffic Signal Control (ATSC)
The static, timer-based traffic light is an artifact of the 20th century. AI-powered Adaptive Traffic Signal Control systems are dynamic networks that learn and optimize in real time. Using data from cameras and sensors at intersections, AI algorithms calculate the optimal green light duration for each approach, adjusting cycle times second-by-second based on actual vehicle and pedestrian volume. For instance, if an intersection detects heavy north-south flow but little east-west traffic, it will intelligently extend the green light in the busy direction while minimizing wait times on the quiet road. These systems are networked city-wide, allowing coordination across hundreds of intersections to create “green waves” that move platoons of vehicles efficiently, eliminating the stop-start driving that causes bottlenecks and excess emissions.
C. The Autonomous Vehicle (AV) Revolution
While adaptive signals manage flow, Autonomous Vehicles represent the ultimate in granular traffic optimization. Human drivers are inherently inefficient they follow at variable distances, accelerate and brake erratically, and make unpredictable decisions. AVs, guided by AI, operate with machine precision. In a fully AV-dominated environment (a state known as “The Singularity of Traffic”), vehicles can communicate with each other (V2V) and with infrastructure (V2I). This allows for:
-
Platooning: AVs traveling closely together in coordinated convoys, dramatically reducing road space used and aerodynamic drag.
-
Harmonized Speeds: Eliminating the “phantom traffic jam” phenomenon caused by one driver’s sudden braking, which creates a shockwave of congestion.
-
Optimal Routing: A central AI system can assign routes to each vehicle to ensure system-wide equilibrium, preventing everyone from being funneled onto the same “fastest” route suggested by conventional GPS apps.
D. AI-Powered Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) Platforms
Congestion is often a result of suboptimal asset utilization millions of private cars, each carrying one person. AI is the engine behind integrated MaaS platforms that combine public transit, ride-sharing, micro-mobility (e-scooters, bikes), and taxi services into a single, user-centric application. The AI algorithm doesn’t just offer options; it performs a continuous, city-scale optimization. It might encourage a user to take a bike to a train station, based on real-time train occupancy and last-mile scooter availability, dynamically pricing the journey to incentivize choices that benefit the overall network. By making multimodal travel seamless and efficient, these platforms reduce the reliance on private car trips, effectively decreasing the total number of vehicles on the road during peak hours.
E. Proactive Incident Management and Infrastructure Monitoring
A significant portion of congestion is non-recurring, stemming from accidents, breakdowns, or road hazards. AI dramatically speeds up incident response. Computer vision algorithms monitor camera feeds 24/7 to automatically detect accidents, stalled vehicles, or debris on the road, instantly alerting authorities. Predictive maintenance models analyze data from infrastructure sensors to foresee potential failures like a bridge stress point or a failing traffic light allowing for repairs before they cause major disruptions. Furthermore, AI can manage the aftermath of an incident by instantly calculating and implementing the optimal diversion plan, updating navigation apps for all affected drivers in real-time.
Global Case Studies: AI in Action Today
The theoretical framework is compelling, but the proof lies in tangible results from pioneering cities.
A. Singapore: The Intelligent Nation
Singapore’s “Smart Nation” initiative features one of the world’s most advanced AI traffic systems. Its AI-powered adaptive traffic light system has reduced average journey times by over 25% at tested intersections. The city-state is also a leader in predictive modeling, using AI to simulate and test the impact of new housing developments or policy changes on traffic before they are implemented, allowing for perfect pre-emptive planning.
B. Pittsburgh, USA: Surtrac’s Scalable Success
In partnership with Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh deployed the Surtrac AI traffic signal system. This decentralized, intelligent system allows each intersection to “talk” to its neighbors and make independent optimization decisions. The results have been staggering: a 25% reduction in travel time, a 40% decrease in idling time (and thus emissions), and even a 20% reduction in vehicular stops. Its success has led to deployments in other U.S. cities, proving the model’s scalability.
C. Barcelona: IoT and AI Synergy
Barcelona’s holistic “Superblocks” model is enhanced by a pervasive IoT sensor network. AI analyzes data from parking sensors, public transit, and traffic cameras to manage flow holistically. The system can guide drivers directly to available parking spots, eliminating the notorious “cruising for parking” that accounts for a surprising 30% of downtown congestion in many cities. This seamless integration of parking and flow management is a prime example of systemic AI thinking.
The Ripple Effects: Beyond Just Smoother Traffic
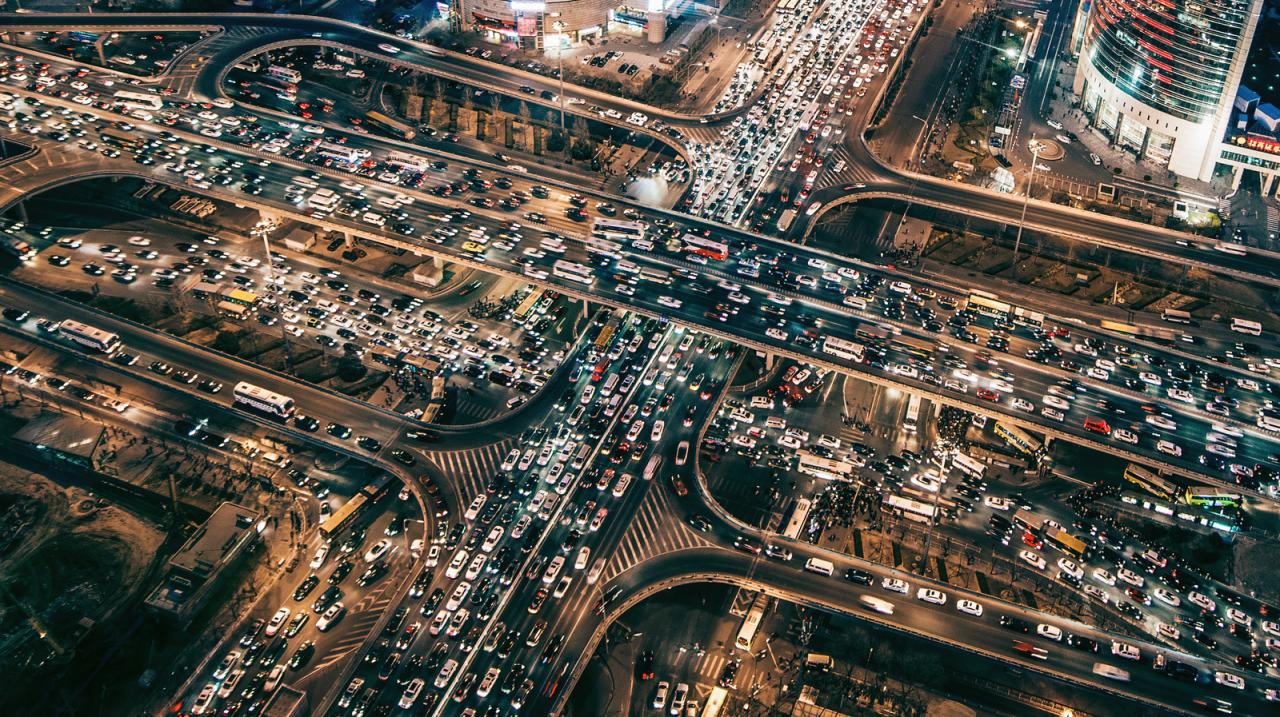

The elimination of traffic congestion via AI catalyzes a cascade of positive externalities that extend far beyond the commute.
-
Economic Productivity: Billions of man-hours currently lost in traffic are reclaimed, boosting economic output. Logistics and supply chains become faster and more reliable, reducing costs for goods and services.
-
Environmental Sustainability: Reduced idling and smoother traffic flows lead to a dramatic drop in greenhouse gas emissions and local air pollutants like NOx and particulate matter. This contributes directly to public health improvements and climate goals.
-
Urban Space Reclamation: With fewer lanes needed for traffic and less space required for parking, vast tracts of urban land can be repurposed into green spaces, pedestrian plazas, bike lanes, and housing, dramatically improving quality of life.
-
Enhanced Safety: AI systems that predict conflict points, coupled with the superior reaction times of autonomous vehicles, have the potential to virtually eliminate the 90%+ of accidents caused by human error, saving millions of lives globally.
Challenges and the Road to Full Integration
Despite the promise, the path to a fully AI-optimized transportation grid is not without significant hurdles that must be thoughtfully navigated.
A. Data Privacy and Cybersecurity: The system’s efficacy depends on massive data collection, raising legitimate concerns about individual privacy and location tracking. Robust anonymization protocols and clear data governance frameworks are non-negotiable. Furthermore, a hyper-connected system presents a high-value target for cyber-attacks, necessitating unparalleled security infrastructure.
B. Infrastructure Investment and Equity: Retrofitting legacy cities with sensors, smart signals, and communication networks requires monumental capital investment. There is a risk of creating a “mobility divide” where only wealthy cities or neighborhoods benefit. Policymakers must ensure equitable access to these technologies as a public good.
C. The Human Transition Period: The most complex phase will be the decades-long transition period where human-driven vehicles, semi-autonomous cars, and fully autonomous vehicles share the road. AI systems must be sophisticated enough to account for unpredictable human behavior during this hybrid era.
D. Ethical Algorithmic Decision-Making: How should an AI system prioritize flow in a crisis? Should it prioritize an ambulance over 50 commuter cars? These ethical frameworks must be programmed transparently and with broad societal consensus.
The Inevitable Future: A World Liberated from Gridlock

In conclusion, the assertion that AI will completely eliminate traffic jams is grounded in demonstrable technology and accelerating deployment. We are moving inexorably toward an era of “Predictive, Autonomous, and Multimodal Mobility.” In this future, your journey will be orchestrated by a benevolent, unseen AI conductor. It will pre-emptively manage intersection signals along your route, guide your autonomous vehicle to seamlessly merge with platoons, and integrate your trip with public transit and micro-mobility options all while dynamically balancing the needs of every other user in the network to maintain system-wide fluidity.
The traffic jam, a defining and frustrating symbol of the industrial and digital ages, is finally meeting its match. It is being out-thought, out-predicted, and out-optimized by artificial intelligence. The result will be more than just faster commutes; it will be the transformation of our cities into more livable, sustainable, and efficient human habitats. The age of congestion is ending, and the age of intelligent mobility has begun. The journey to this future is already underway, and its destination is a world where the term “rush hour traffic” is a curious historical footnote, not a daily reality.